Learn this concept that can help score AL1 in Math PSLE (Simultaneous Equation)
 By Haris Samingan
By Haris Samingan 
How would you solve this question:
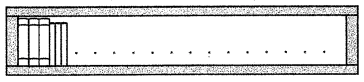
A shelf can be packed from end to end with 30 large books or 45 small books. Kevin already packed the shelf with 3 large books and 23 small books. At most, how many more large books can Kevin pack the shelf with?
Well, you probably can guess from the title. We can solve it using Simultaneous Equation
What is a Simultaneous Equation Concept Question?
A Simultaneous Equation concept question is a type of word problem where two different items take up the same space or have the same total.
For example:
- A shelf can fit 30 large books OR 45 small books
- Both options fill up the exact same shelf space
The key idea is that you can compare the two items because they equal the same amount. This lets you find out how much of one item equals the other item.
How to Spot a Simultaneous Equation Concept Question
You can tell it's a Simultaneous Equation concept question when you see:
- Two different types of items that can fill the same space or amount
- Words like "or" that show different ways to fill the same thing (30 large books OR 45 small books)
- The same total or space being used in different ways
- You need to convert between the two types of items
If the problem tells you different ways to use the same space or reach the same total, it's probably a Simultaneous Equation problem.
Example Question 1
Problem (PSLE 2022 Paper 2 Q3): A shelf can be packed from end to end with 30 large books or 45 small books. Kevin already packed the shelf with 3 large books and 23 small books. At most, how many more large books can Kevin pack the shelf with?
Example Question 1 Solution
Follow these steps to solve Simultaneous Equation problems:
Step 1: Write Down What You Know
Use letters to represent each type of item, then write an equation showing they are equal.
For the books problem:
- Let L = large books
- Let S = small books
Since both fill the same shelf: 30L = 45S
Step 2: Find the Value of One Item
Convert one type of item into the other type. Usually, find what 1 of the smaller item equals.
We want to know what 1 small book equals in terms of large books:
45S = 30L
1S = 30 ÷ 45
1S = 2/3L
This means 1 small book takes up the same space as 2/3 of a large book.
Step 3: Convert the Items You Have
Change the items in the problem to the same type.
Kevin has 23 small books. Let's convert to large books:
23S = 2/3L × 23
23S = 15 1/3L
So 23 small books take up the same space as 15 1/3 large books.
Step 4: Calculate the Remaining Space
Find how much space is left and convert to the answer the question wants.
The shelf can fit 30 large books total.
Kevin already used:
- 3 large books
- 23 small books (= 15 1/3 large books)
Space remaining:
30 - 3 - 15 1/3 = 11 2/3 large books
Since you can't pack a fraction of a book, round down:
Answer: 11 large books
Check Your Answer
Let's verify:
- 3 large books + 23 small books + 11 more large books
- Total large books = 3 + 11 = 14 large books
- 23 small books = 15 1/3 large books (in space)
- Total space used = 14 + 15 1/3 = 29 1/3 large books ✓
- This is less than 30, so it fits!
Example Question 2
This question typically shows in weighted assessment, end of year exams, prelims and PSLE.
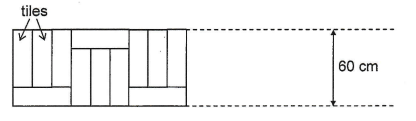
Problem (PSLE 2014 Paper 2 Q13): The diagram shows how tiles are arranged in a repeated pattern along an 18 m wall. The length and breadth of each tile add up to 60 cm. The length of each tile is 3 times its breadth. How many tiles are needed to cover the entire wall?
Example Question 2 Solution
Step 1: Write Down What You Know
Use letters to represent the length and breadth, then write equations.
For the tiles problem:
- Let L = tile's length
- Let B = tile's breadth
From the problem:
- (Equation 1) 1L + 1B = 60
- (Equation 2) 1L = 3B
Step 2: Substitute One Equation Into the Other
Replace one unknown with the other equation.
Substitute Equation 2 into Equation 1:
3B + 1B = 60
4B = 60
1B = 60 ÷ 4 = 15 cm
Step 3: Find the Other Unknown
Use the value you found to calculate the other measurement.
1L = 3B
1L = 3 × 15
1L = 45 cm
Step 4: Find the Pattern Length
Look at the repeating pattern to find how long one group is.
From the diagram, 1 group length = 45 cm
1 group has 4 tiles
Step 5: Calculate the Total
Convert the wall length to the same units, then find how many groups fit.
Wall length = 18 m = 1800 cm
Number of groups = 1800 ÷ 45 = 40 groups
Total tiles = 40 × 4 = 160 tiles
Tips to Remember
- Set up equations from the information given - Look for relationships between items (like "add up to" or "is 3 times")
- Use substitution when you have two equations - Replace one unknown with an expression from another equation
- Convert everything to the same units - Change metres to centimetres, or vice versa
- Look for repeating patterns - Count how many items are in one group, then multiply
- Watch out for fractions - Real-life items often need whole numbers, so round down when needed
- Think about what "at most" means - It means the maximum whole number that fits
Why Does This Work?
Simultaneous equations work because we have two pieces of information about the same items.
In Example 1, both types of books fill the same shelf, so we can compare them directly.
In Example 2, we know both that the length and breadth add up to 60 cm AND that the length is 3 times the breadth. Having two facts lets us find both unknowns.
By using substitution (putting one equation into another), we can solve for one unknown first, then use that answer to find the other unknown.
This is like knowing that 2 small pizzas = 1 large pizza, and also knowing the total cost. With both pieces of information, you can figure out the price of each type!
